Untuk Pembelajaran selanjutnya…
(Untuk UN 12 SMA dan TOEFL Test)
Listening adalah salah satu kompetensi dasar yang wajib dikuasai oleh mereka yang ingin mempelajari bahasa Inggris atau setidaknya syarat tersebut pasti berlaku ketika kita sedang melakukan komunikasi dalam bahasa Inggris (English conversation). Skill listening itu tidaklah didapatkan secara instan (dalam satu atau dua hari/minggu), kita harus terbiasa mendengarkan ujaran bahasa Inggris sedini dan sesering mungkin sehingga lambat laun skill mendengar kita akan terasah. Berikut adalah strategi melatih skill listening yang bagus:
- Mendengarkan lagu bahasa Inggris memang bagus, namun mendengarkan percakapan atau pidato bahasa Inggris jauh lebih bagus karena pengucapan (pronounciation) antara lagu dan percakapan biasa berbeda. Pronounciation kata per kata alam sebuah lagu terkadang tidak menerapkan aspek-aspek fonetis yang tepat.
- Jika masih dalam tahap belajar, jangan langsung mendengarkan level ujaran bahasa Inggris dari yang level pronounciation-nya cepat dulu (fast pronounciation), seperti “Rapper’s pronounciation”, tapi coba dulu dari yang level pronounciation-nya standar dulu, seperti yang sering digunakan dalam percakapan-percakapan sehari-hari.
- Dengarlah ujaran bahasa Inggris tipe British English dulu karena tipe American English lebih banyak terkontaminasi oleh bahasa gaul (Slang language) yang rata-rata infomal namun tidak universal, dan kadang-kadang sedikit sarkas (kasar)
Ada tiga kategori dalam Listening Section:
- Dialogues (Dialog) → Listening for UN dan TOEFL
- Finding the relevant pictures (Menemukan gambar yang berhubungan) → Listening for UN only
- Short and long monologues (Monolog singkat dan panjang) → Listening for UN dan TOEFL only.
DIALOGUES
Dalam bagian dialogue, kamu harus bisa mengidentifikasi informasi detail (5W + 1H) yang diucapkan oleh first speaker atau second speaker.
| Keyword: Dalam dialogue, informasi penting yang ditanyakan (what, who, when, where, why, how) biasanya terdapat dalam jawaban/respon dari pembicara |
You will hear:
Man : Would you like to join my graduation party?
Woman : I am sorry. I wouldn’t. My father was just hospitalized. I have to stand by there for unknown time.
Man : That’s pity on him. I hope he will get better soon.
(Question: Why can’t the woman join the man’s graduation party?)
Pertanyaan yang sering ditanyakan dalam section 1 (Listening for dialogue part) adalah:
- The topic of the dialogue (Topik teks)
- Kind of expressions (Jenis ungkapan)
- Response of the expression (Respon dari ungkapan)
- Setting of the dialogue (Latar tempat (place), waktu (time), person (orang), kondisi (Condition), dan alasan (Reason)
Semuanya dirangkum dalam format pertanyaan 5W+1H?
Dialogues related to expressions use
Dalam hal ini, kamu diharuskan memahami konsep expressions (ungkapan) yang digunakan dalam percakapan bahasa Inggris. Ungkapan yang paling sering digunakan adalah sebagai berikut:
Expressions of apologizing (Ungkapan minta maaf)
I apologize for/ please forgive me for/ Pardon / I am terribly sorry / I am sorry (Decreasing intonation)
Responses:
That’s ok / Forget it! / That is fine
Expressions of satisfaction (Ungkapan kepuasan)
I get (am) satisfied with / It is satisfying me / I am not disappointed with that / I really enjoyed that
Responses:
Thanks!
Expressions of dissatisfaction (Ungkapan ketidakpuasan)
I am dissatisfied with / I get disappointed / you are disappointing me
Responses:
I am sorry for that. Next time, we will be better than now
Expressions of sympathy (Ungkapan bersimpati)
I’m sorry to hear that/ How terrible / Poor you!/ that’s shame / That’s (too) bad / How awful + I hope ….
Response:
I hope so. Thanks for your sympathy.
Expressions of asking for help (Ungkapan meminta tolong)
Would you..?/ Could You..?/ Do you mind if you..?/ Would you mind + verb (-ing)..?
Responses:
Of course, with a pleasure (accept the request)
Sorry, I can’t help you / Sorry I’m busy now (refusing the request)
Situation: I think it is ../ do you agree if ….?
Expressions of agreement (Ungkapan setuju)
I agree / It sounds nice / That is good idea / I approve of /
I am with you / I think so / I am in you words / I can agree more / I am on your side / THAT’S VERY GOOD
Situation: I think it is ../ do you agree if ….?
Expressions of disagreement (Ungkapan tidak setuju)
I disagree/ It sounds bad/ That’s bad idea/ I disapprove of / I don’t think so / No way
Expressions of asking for opinion (Ungkapan meminta opini)
What is your opinion about? / What is your view on? / What do you say about? / What if…? / What do you think about?
Responses:
I think…/ In my view, …/ In my own opinion…./ Based on …/ According to…/ In accordance with …
Expressions of offering help (Ungkapan menawarkan bantuan)
May I help you?/ What can I help you?/How can I be of help to you? / What can I do for you?
Responses:
Please, take me / give me /help me to / I need a (accepting an offer)
No thanks (Refusing an offer)
Expressions of giving advice (Ungkapan memberi saran)
It’s best to / You should / You ought to / Why don’t you? / What if you…? / You had better to.
Response:
Thanks for your advice.
Expressions of thanking (Ungkapan berterima kasih)
Thank you/ thank you very much/I’m grateful for your…
Responses:
You are welcome / Never mind / Don’t mention it!
Expressions of praising / compliment (Ungkapan memuji)
You are (great / wonderful / marvelous)/ What a great! / What a good job! / You are so beautiful with that ….
Responses:
Thanks! / I am nothing without you all / I am just an ordinary person / this is cheap / this is not special!
Keyword: Pahamilah situasi untuk memberikan ungkapan dan merespon ungkapan:

You will hear:
Man : Why do you look so sad? (Situation 1)
Woman : My husband just lost his job. (Situation 2 )
Man : I am sorry to hear that I hope he will get a better one. (Expression)
Woman : _________________! (Response of expression)
(Question : What will the woman probably say?)
- I hope so. Thanks
- Everything becomes so terrible
- I’d like it
- Don’t be say that, please!
Jawaban: A (Respon dari ungkapan bersimpati adalah I hope so. Thanks)
FINDING THE RELEVANT PICTURE
Menentukan gambar yang dimaksudkan dalam listening UN tidaklah sulit. Kamu harus memahami GAMBAR berdasarkan pemaparan yang diungkapkan lewat dialog. Biasanya pemaparan benda terdapat di bagian penjelasan terpanjang. Ada tiga tipe relevant picture yang ditanyakan:
- Picture based on its physical characteristics (ciri-ciri fisik)
- Picture based on its relevance with fields (hubungannya dengan bidang pekerjaan)
- Picture based on its function (fungsi atau kegunaannya)
You will hear:
Man : You know that Jean is now looking for a job. But I can’t help her due to my unknowing her field background.
Woman : How is her special field?
Man : I am not sure. As far as I know, at the time, she looked like a doctor wearing a white dress. Her previous job was related with medicines and she always stayed up in a drugstore.
Woman : Oh, I see.
[Question: What job (picture) indicated jean’s previous job?]
See the picture of “PHARMACIST”. Ia seorang apoteker.
SHORT / LONG MONOLOGUE
Dalam konteks monolog pendek atau panjang, kita harus pandai menangkap informasi penting yang kemungkinan besar akan ditanyakan dalam soal. Namun kemampuan menyimak non-native English speaker tidak sebaik native English speaker.
Tipsnya: Catatlah detail informasi (5W + 1H) yang dituturkan sang pembicara.
- What (biasanya berupa aspek non-humanistik yang muncul dalam bentuk definisi atau yang lain-lain)
- Where (biasannya menunjukan tempat atau arah dan muncul setelah preposisi on, in, at, from, to, toward, etc)
- When (indikasi berupa time series, minute, hour, day, year, etc atau berua konjungsi waktu after, before, when. while, since, for, etc)
- Why (indikasi berupa reason/alasan, because (of), due to, so that, etc)
- Who (indikasi berupa referensi orang atau nama)
- How (indikasi berupa aspek numerik. Hati-hati, dalam soal tidak dimaksudkan secara gamblang aspek numeric yang ditanyakan. Kita biasanya harus melalui proses penghitungan yang sederhana (multiplication, division, subtraction, addition )
Contoh:
- The teacher is 34 in age/years old and now is 2013. When was he born? 2013-34 =1989
- Thirty kilograms plus/ is added by ten kilograms equals? Forty kilograms (penambahan)
- Thirty miles minus/is substracted by ten miles equals? Twenty miles (pengurangan)
- Twenty thousand times/is multiplied by ten equals? Twenty hundreds thousand (perkalian)
- Ten thousand is divided by twenty is five hundreds. (pembagian)
Contoh lain dari long monologue:
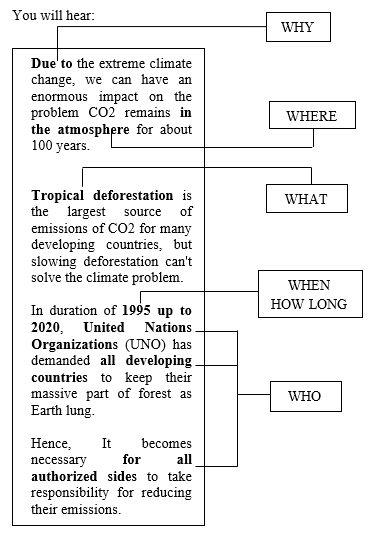
Questions number 1-5
- What becomes the source of CO2 emissions?
- Why does problem of COC remain in atmosphere during 100 years?
- How long does United Nation Organization (UNO) demand all developing countries to keep their forests?
- Who is the most responsible sides to reducing the problem of emission?
- Where does the process of CO2 emission occur?
Jawaban
- Tropical deforestation (pembalakan hutan)
- Extreme climate change (perubahan iklim ekstrem)
- 25 years (2020-1995 = 25 years)
- All authorized sides (semua pihak terkait)
- In the atmosphere (di atmosfer)
Semoga Bermanfaat
